Deployment and configuration¶
Before diving into the specifics we are going to deploy the current infrastructure. To do so we will be using Docker and docker-compose.
Note
Docker is an open platform for developing, shipping, and running applications. Docker enables you to separate your applications from your infrastructure so you can ship and deliver software quickly.
First thing is to clone the repository containing the docker-compose files and necessary configuration files.
git clone https://gitlab.com/radiology/infrastructure/medical-imaging-demo.git
cd medical-imaging-demo
docker-compose pull
docker-compose build
docker-compose up -d
docker-compose ps
After the docker-compose ps command, you will see which services are
up and running as shown below. Look for the “Up” state.
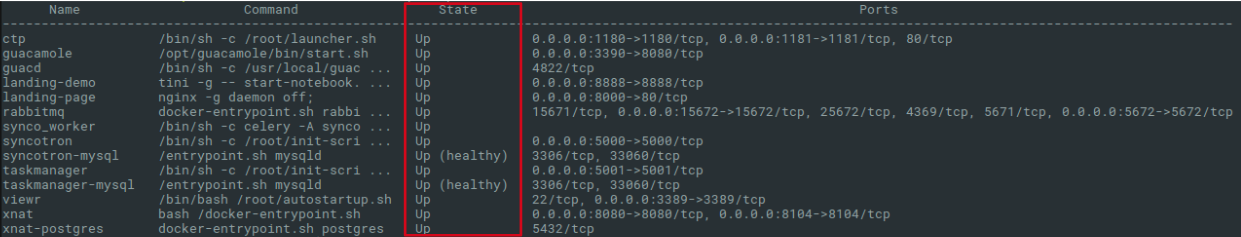
If all services are up and running you can continue. Check the landing page by using a web browser and going to the IP address of the machine running the Demo. This could be the IP address of the tutorial machine you got, or just localhost if running the tutorial locally on your linux machine, or if your are running on a Mac/Windows it is the IP of your docker-machine.
Note
In your browser type the ip-address/hostname followed by a colon and port 8000 ie: http://192.168.99.100:8000 This should open a webpage showing the same overview as above, this is called the landing page. We will use this landing page to switch between the different services.
Mac/Windows/Virtual: In your browser, type the IP-address/hostname followed by a colon and port 8000 ie: http://192.168.99.100:8000
Linux: http://localhost:8000
Note
In a local machine, make sure you are running docker as root, you can use sudo usermod -aG docker <your-user>